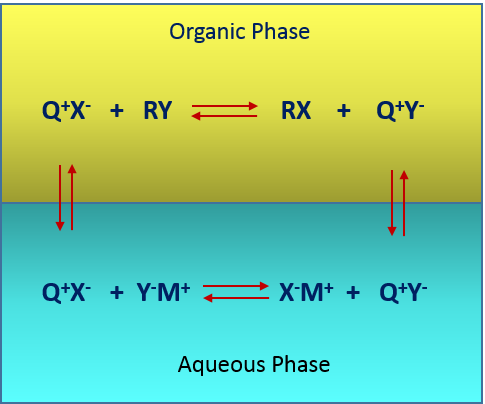
CatOnium phase transfer catalysts (PTC) are quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts, which are widely used in the production of:
 |
||
In addition CatOnium Phase Transfer Catalysts are also used in polymer modifications and pollution treatment and the removal or destruction of impurities in
wastes and product streams.
Typical reactions where CatOnium phase transfer catalysts are employed include:
Displacements reactions using:
Benefits
The use of phase CatOnium phase transfer catalysts offers number of benefits from synthetic, economic, manufacturing and engineering point of view. This includes:
Most common CatOnium PTC’s are quaternary ammonium salts containing either alkyl or mixed alkyl/aryl groups. Their applicability is restricted by the thermal stability which is limited to about 100°C. CatOnium phase transfer catalysts comprises broad range of quaternary ammonium halides, with F–,Cl–,Br– and I– as counter anions, and limited number of quaternary hydroxyl ammonium compounds, with an OH– group as counter anion.
Phosphonium PTC’s are used in the cases in which the use of ammonium compounds is not suitable because of their thermal instability.
The thermal stability of CatOnium quaternary phosphonium salts is quite good in a range between 120-150°C, with indications that they can be also used at temperatures up to 200 °C.
| CatOnium BeTPC |
CAS Number: 1100-88-5 Benzyltriphenylphosphonium Chloride |
Epoxy Resins, Fluoroelastomers, Powder Coatings |
| CatOnium BTPB |
CAS Number: 1779-51-7 Butyltriphenylphosphonium Bromide |
Epoxy Resins, Fluoroelastomers, Powder Coatings |
| CatOnium BTPC |
CAS Number: 13371-17-0 Butyltriphenylphosphonium Chloride |
Pharmaceuticals, Powder Coatings |
| CatOnium ETPAAC |
CAS Number: 35835-94-0 Ethyltriphenylphosphonium Acetate |
Epoxy Resins |
| CatOnium ETPB |
CAS Number: 1530-32-1 Ethyltriphenylphosphonium Bromide |
Epoxy Resins, Fluoroelastomers, Powder coating resins, Powder Coatings |
| CatOnium ETPI |
CAS Number: 4736-60-1 Ethyltriphenylphosphonium Iodide |
Epoxy Resins, Fluoroelastomers, Powder Coatings |
| CatOnium MTPB |
CAS Number: 1779-49-3 Methyltriphenylphosphonium Bromide |
Powder Coatings |
| CatOnium TBAB |
CAS Number: 1643-19-2 Tetrabutylammonium Bromide |
Fluoroelastomers, Herbicides, Powder Coatings, Zeolites |
| CatOnium TPAB |
CAS Number: 1941-30-6 Tetrapropylammonium bromide |
Pharmaceuticals, Zeolites |
| CatOnium TPPBr |
CAS Number: 2751-90-8 Tetraphenylphosphonium Bromide |
Fluoroelastomers, Pharmaceuticals, polyacrylate polymers |

